Let it be light
What is LED and why do we hear these three letters all the time? The story starts at the beginning of 20th century. In a world where everyone used gas lamps and candles for lighting, scientists began to develop a more practical solution, which subsequently changed the world. They set the main idea for the incandescent filament bulb. There had already been a clear idea of how it would look, what kind of principle it would function on, what kind of wire it would have, but there was one problem – it did not sustain light for long.
Here comes the contribution of Thomas Edison, who in 1879 found out that the air from the glass balloon should be withdrawn and the incandescent filament should be made of tungsten in order to achieve long illumination and higher efficiency of the bulb.
After the bulb’s invention, scientists found another effect of lighting – fluorescence. George Gabriel Stokes first noticed the phenomenon in 1852, and in 1934 Arthur Holly Compton, from General Electric, had a successful attempt with fluorescence lighting which led to the first prototypes of the luminescent lamp. Despite the dominance of the incandescent lamp, the 20th century has led to a number of discoveries in the sphere of lighting. The second half of the century leads to the invention of Halogenated High-Intensity Discharge Lamps (HID). It represents an electric lamp with a gas-discharge emitter. The latter one produces light by creating electric arc between tungsten electrodes. It was widely used in the early 1990s for car headlights, bicycles, lanterns and other similar lighting fixtures. In response to the oil crisis in 1973, Edward Hammer, a General Electric engineer, invented the CFL – Compact fluorescent lamp. It appeared in 1976, known as energy saving. Its innovative design and working principle were copied by other producers, which resulted in its mass production. Although it was invented after the 50s and refined at the beginning of this century, LED lighting is explicitly here to stay.
What is LED and how does LED work?
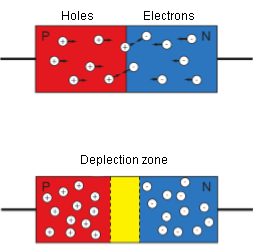
What is LED? The LED-Light Emitting Diode is a semiconductor diode which consists of areas with positive and negative transistors and p-n transition. It radiates non-coherent light in a narrow spectrum when an energy current flows through it. The diode uses one piece of N-type material (with an excess of electrons) connected to another part of P-type material (with excess of ‘holes’). The place where the two elements meet is called transition.
Initially, the N material has more electrons, and the P material has fewer. This creates an imbalance, where electrons and holes begin to move toward each other during the transition, attracted by their opposite electrostatic charges.
When a hole and an electron meet, they neutralize each other, forming a neutral zone of connected holes and electrons. When connecting the P-type material to the positive pole and N-type respectively to the negative pole of a power supply, this generates an electric field in the diode. This causes the free electrons to be attracted to the positive electrode and repelled by negative.
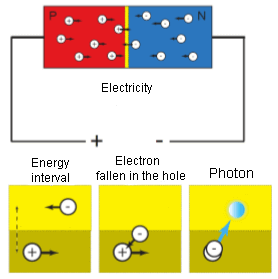
If we raise the voltage sufficiently high, the electrons that are quietly sitting in the holes in the depletion area are discarded. As a result, the area is eliminated and all the electrons and holes begin to move again. When an electron falls into a weaker energy hole, it must somehow lose excess energy. So, this energy is given as a photon – the basic unit of light. The difference in energy levels determines the energy and strength of the photon (the power of lighting).
The Fathers of the LED
In 1906, a British scientist called Henry Rotund of Marconi Laboratories discovered that the semiconductor compound produces light – electroluminescence. In the 50s of the 20th century, other British scientists experimented in electro-luminescence. They used a semiconductor called gallium arsenide (GaAs), which led to the development of the first infrared diode. In 1962 Nick Holonak of General Electric created the first visible light spectrum that lights in red. This discovery won him the name ‘Father of the LED’
Later, along with his former student, George Krafford, they invented the first yellow LED and ultimately a much brighter red-orange LED. The 80s of the last century are labeled with the creation of a LED made of gallium-aluminum-arsenide. Through it red, yellow, orange, and green light could be produced. It could light 10 times brighter than the old LED models.
Why is the white LED delayed? What is LED with white light?
Depending on the used semiconductor, the colours of the LED light are:
AlGaAs – red, infrared;
AlGaP – green;
AlGaInP – orange-red, orange, yellow and green;
GaAsP – red, orange-red, orange and yellow;
GaP – red, yellow, green;
GaN – green, blue;
InGaN – near UV, blue-green, blue;
SiC – blue;
Al2O3 – blue;
ZnSe – blue;
AlN,
AlGaN,
AlGaInN – from the near to the distant ultraviolet
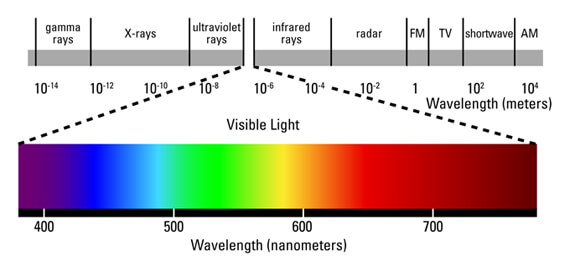
Although the first LED was produced in the 1960s of the last century, the white one appeared at the end of the 20th century. This is due to the fact that all LEDs emit in very narrow spectrum of light. White light is a set of all the spectra of the the visible light. In practice, all colors are embedded in white – starting with red (immediately after the infrared spectrum), passing through yellow, green, and reaching to blue before the ultraviolet spectrum.
The first attempts to create a white LED are based on RGB technology. Combining red, blue and green LEDs produces white light. This technology, however, turns out to be extremely expensive and not applicable to mass distribution.
LED Innovators
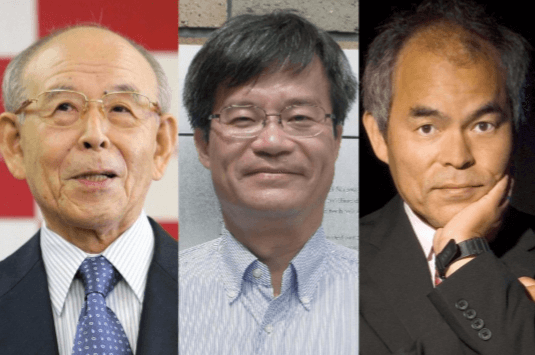
In 1991, Isamu Akasaki, Hiroshi Amano and Shuji Nakamura invented the white LED using blue and UV LED. For this discovery they won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2014.
” The incandescent lamps lit up the 20th century, the 21st century will be illuminated by LED lamps! ” –
– notes the Nobel Committee
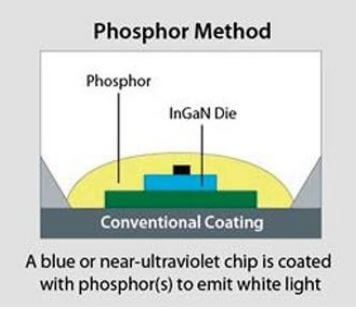
The three Japanese found the principle of using phosphorous material for converting monochrome light from blue or ultraviolet LED into wide-spectrum white light. Fluorescent light is similar to them.
What is LED with white light?
For the light emitting diodes based on phosphorus material, the LEDs are covered in one color (most common blue LEDs from InGaN Indian gallium nitride) with phosphorus in different colors in order to produce white light and obtain the so-called white LED based on phosphorus.
Depending on the color of the original LED, phosphors in different colors may be used. If several phosphor layers of different colors are applied, the radiated spectrum expands by increasing the value of the color rendering index (CRI) of the specific LED.
LED applications
Just two decades ago, the LED modules were only applied in limited electronic devices such as: remote controls, emergency exits, and indication and illumination of control devices.
Nowadays things look different. LED lighting is becoming more and more commonly applied in both industry and household. They offer countless LED home solutions, lighting of gas stations, halls, metro stations, etc.,automotive industry, for indoor and outdoor LED advertising.
Now we do not even ask ourselves ‘What is LED?’. We’re so accustomed to the LED technology – virtually anywhere around us is LED technology – lighting, TVs, remote controls, laser epilators, infrared massagers, and many more.